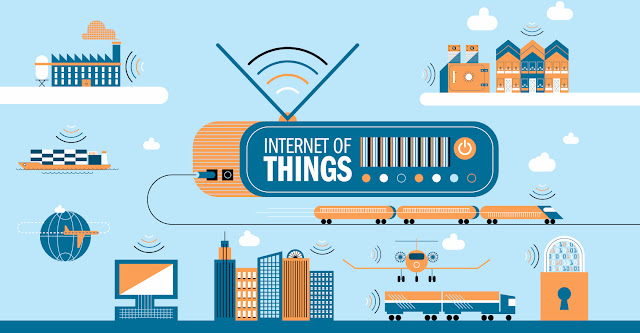
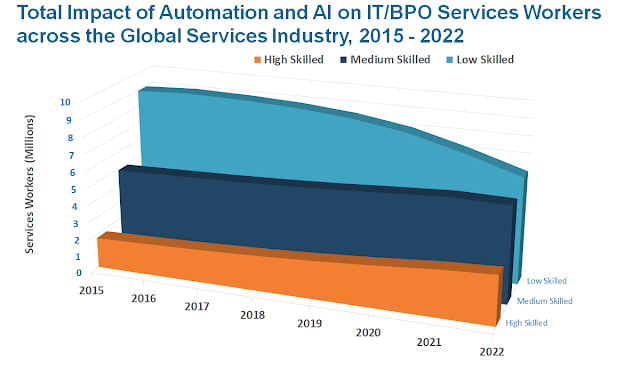
This new wave of connectivity is going beyond laptops and smartphones, it’s going towards connected cars, smart homes, connected wearables, smart cities and connected healthcare. Basically a connected life. Practical applications of IoT technology can be found in many industries today, including precision agriculture, building management, healthcare, energy and transportation etc.
Applications of IoT in the real world
Smart home:
Smart Home is the most searched IoT associated feature on Google. Smart Home clearly stands out, ranking as highest Internet of Things application on all measured channels. More companies are active in smart home than any other application in the field of IoT. Smart Home has become the revolutionary ladder of success in the residential spaces and it is predicted Smart homes will become as common as smartphones. The cost of owning a house is the biggest expense in a homeowner’s life. Smart Home products are promised to save time, energy and money. With Smart home companies like Nest, Ecobee, Ring, August, AlertMe, Philips, Haier and Belkin to name a few, will become household brands and are planning to deliver a never seen before experience.
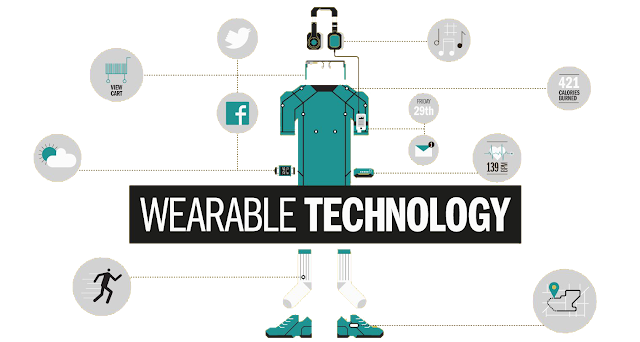
Wearables:
Wearables have experienced a explosive demand in markets all over the world. Wearable technology is a hallmark of the Internet of Things and the most ubiquitous of its implementations to date. The efficiency of data processing achieved by various smart wristwear, hearables, and smart glasses is gradually dispelling inert skepticism among the public and is getting closer to where wearables will bring exceptional value to our lives.
Wearable devices are installed with sensors and softwares which collect data and information about the users. This data is later pre-processed to extract essential insights about user. These devices broadly cover fitness, health and entertainment requirements. The pre-requisite from internet of things technology for wearable applications is to be highly energy efficient or ultra-low power and small sized.
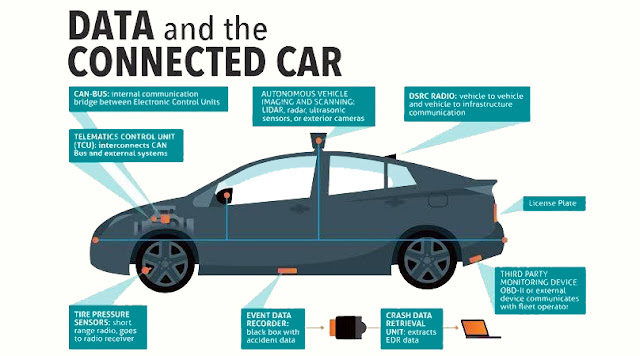
Connected car:
The Internet of Things is breaking fresh ground for car manufacturers by introducing entirely new layers to the traditional concept of a car. This upgrade the connected, smart car comes as a revolutionary way to drive and stay in touch with the world around at the same time. By offering a fancy-free variety of infotainment services and connected car applications for drivers, the automotive industry has the potential to become an IoT champion among other industries and fuel the IoT cloud services adoption among car owners and walkers alike. A connected car is a vehicle which is able to optimize it’s own operation, maintenance as well as comfort of passengers using onboard sensors and internet connectivity.
Connected Health:
The internet of things has numerous applications in healthcare, from remote monitoring to smart sensors and medical device integration. It has the potential to not only keep patients safe and healthy, but to improve how physicians deliver care as well. Healthcare IoT can also boost patient engagement and satisfaction by allowing patients to spend more time interacting with their doctors.
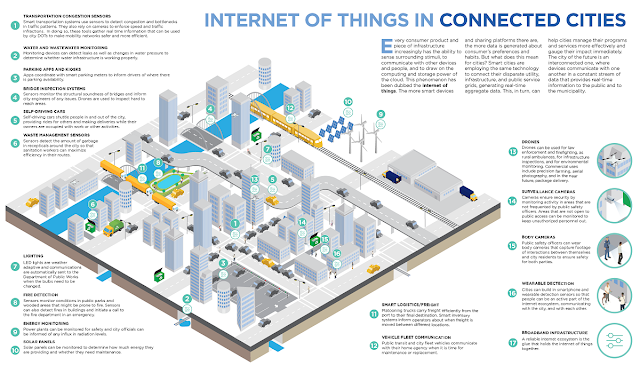
Smart City:
Smart City is the product of accelerated development of the new generation information technology and knowledge-based economy, based on the network combination of the Internet, telecommunications network, broadcast network, wireless broadband network and other sensors networks where Internet of Things technology (IoT) as its core. Smart city spans a wide variety of use cases, from traffic management to water distribution, to waste management, urban security and environmental monitoring. Its popularity is fueled by the fact that many Smart City solutions promise to alleviate real pains of people living in cities these days. IoT will solve major problems faced by the people living in cities like pollution, traffic congestion and shortage of energy supplies etc. By installing sensors and using web applications, citizens can find free available parking slots across the city. Also, the sensors can detect meter tampering issues, general malfunctions and any installation issues in the electricity system.
Industrial internet:
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the use of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in manufacturing. Also known as the Industrial Internet, IIoT incorporates machine learning and big data analytics, harnessing the sensor data, machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and automation technologies that have existed in industrial settings for years to create brilliant machines.
The driving philosophy behind IIoT is that, smart machines are more accurate and consistent than humans in communicating through data. And, this data can help companies pick inefficiencies and problems sooner. IIoT holds great potential for quality control and sustainability. Applications for tracking goods, real time information exchange about inventory among suppliers and retailers and automated delivery will increase the supply chain efficiency.
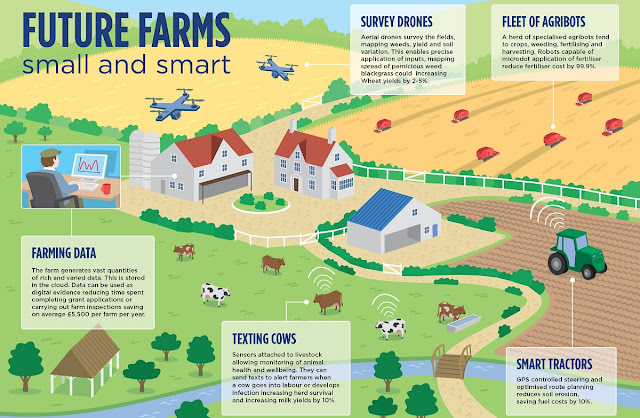
Smart farming:
With the continous increase in world’s population, demand for food supply is extremely raised. Governments are helping farmers to use advanced techniques and research to increase food production. Smart farming is one of the fastest growing fields in IoT. Smart farming based on IoT technologies will enable growers and farmers to reduce waste and enhance productivity ranging from the quantity of fertilizer utilized to the number of journeys the farm vehicles have made.
In IoT-based smart farming, a system is built for monitoring the crop field with the help of sensors (light, humidity, temperature, soil moisture, etc.) and automating the irrigation system. The farmers can monitor the field conditions from anywhere. IoT-based smart farming is highly efficient when compared with the conventional approach.